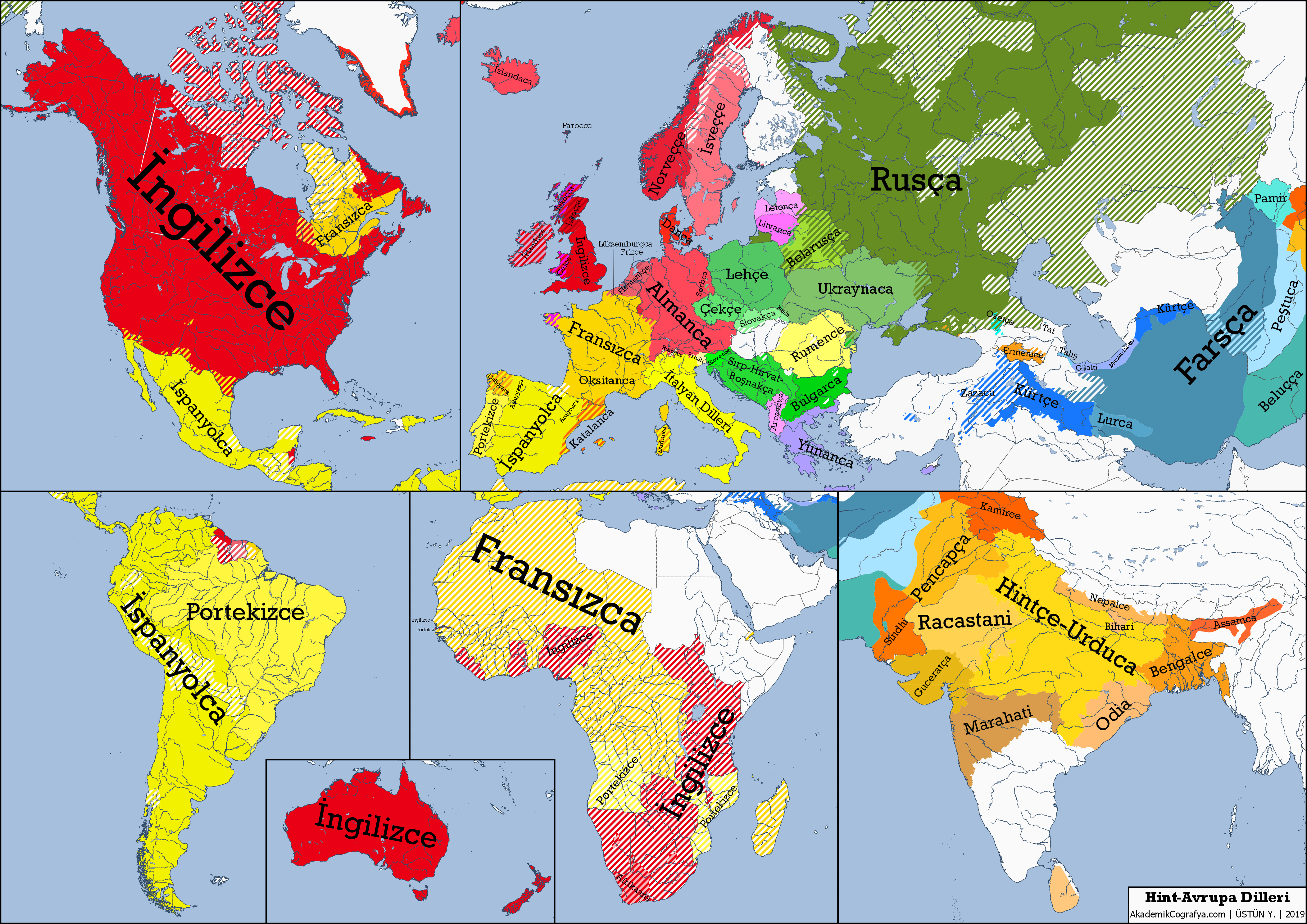
The Indo-European languages form a remarkable family of tongues that includes over 400 languages spoken by roughly 40% of the global population today. Emerging from the depths of history, these languages trace their roots back to a group of people known as the Caucasus Lower Volga, who thrived in today’s Russia around 6,500 years ago during the Eneolithic period. Recent groundbreaking studies utilizing ancient DNA research have shed light on the linguistic origins of these populations and their profound impact on cultural traditions. Researchers link them to the storied Yamnaya culture, renowned for their nomadic pastoralism and pioneering advancements in harnessing the bioenergy of the Eurasian grasslands. As the narrative of proto-Indo-European speakers unfolds, it becomes a fascinating exploration of humanity’s early connections across vast landscapes and across time.
Known collectively as the proto-Indo-European continuum, these ancient languages encompass a wide spectrum of dialects that have influenced countless cultures around the world. Exploring this linguistic family reveals a tapestry woven from various threads of history, including connections to the Yamnaya civilization, significant archaeological findings, and advancements in genetic studies. Linguists, anthropologists, and geneticists converge on this topic, unearthing relationships between the populations of the Caucasus Lower Volga and the ancestral languages that shaped modern European and Asian tongues. The research suggests a rich interplay of demographics and language evolution, greatly expanding our understanding of how language spread and diversified over millennia. The implications of these findings continue to resonate, illustrating the complex interplay between migration and language development.
The Genetic Legacy of the Yamnaya Culture
The Yamnaya culture, originating from the lower Volga region approximately 6,500 years ago, significantly contributed to the genetic and linguistic evolution of modern Europeans. Advanced ancient DNA research has spotlighted the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who played a crucial role in the dispersal of the Proto-Indo-European language family. Their nomadic lifestyle and innovative pastoral practices, including horseback riding and using oxen-towed wagons, facilitated their expansive migrations across the Eurasian steppes, which in turn spread their linguistic and cultural traits across vast distances.
This research supports the premise that the Yamnaya were not merely population layers within Europe but a significant force behind the demographic transformations observed. These communities intermingled with local populations, contributing to the genetic diversity in contemporary European genetics. Thus, understanding the Yamnaya culture provides excellent insights into the origins of numerous languages, highlighted by their ability to mix traditional practices with new advancements, illustrating a dynamic cultural interchange.
The Role of DNA Evidence in Linguistic Research
Recent studies leveraging ancient DNA have transformed our understanding of the linguistic roots within Indo-European languages. By mapping genetic data from archaeological sites in the Caucasus Lower Volga region and beyond, researchers can trace how these populations interacted with others, laying the groundwork for modern language families. This intersection of genetics and linguistics illustrates the complexities involved in the expansion of languages like those of the Yamnaya, enriching our comprehension of human history.
Advancements in DNA analysis techniques have allowed scientists to recover and interpret genetic materials that were previously inaccessible. The evidence showing a profound mixing event among different populations, including the Yamnaya, reframes historical narratives, revealing continuous cultural evolution rather than static population movements. Such findings emphasize the importance of ancient DNA research in not just confirming linguistic hypotheses, but also in unraveling the shared cultural heritage of modern populations.
Tracing the Origins of Proto-Indo-European Languages
The origins of Proto-Indo-European languages are a captivating subject that links archaeological findings with linguistic evolution. Recent genetic studies have identified the Caucasus Lower Volga as a significant epicenter for these languages, suggesting that the speakers migrated and integrated with neighboring cultures. The linguistic similarities observed among languages as diverse as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit can now be linked to these early populations in a geographically and temporally distinct context.
Such discoveries shed light on the widespread dissemination of Indo-European languages through both migration and cultural exchange. Rather than a singular event, the emergence of these languages was a complicated process involving several waves of interactions across Eurasia. Each linguistic branch, from Celtic to Indo-Aryan, carries fragments of these ancient narratives, demonstrating how interconnected human societies have been throughout history and highlighting the rich tapestry of our shared linguistic heritage.
The Impact of Archaeological Discoveries on Language Evolution
Archaeological discoveries have historically played a key role in deciphering the evolution of languages. Excavations at sites linked to the Yamnaya culture have provided a wealth of material evidence which, when combined with genetic findings, deepen our understanding of linguistic development. The kurgans or burial mounds associated with these cultures serve as vital touchstones for understanding social practices and cognitive frameworks that underlie language use.
Additionally, these archaeological findings guide researchers in reconstructing languages through a more comprehensive view of cultural practices and societal structures. For instance, the discovery of tools, artifacts, and remnants of habitation provide contextual frameworks that elucidate how early peoples communicated. Such synergies between language, culture, and archaeology are invaluable in tracing the roots of the Indo-European languages.
Linking Ancient DNA Research to Modern Linguistics
The integration of ancient DNA research with modern linguistics paves the way for a more cohesive narrative of language ancestry. Studies examining Caucasus Lower Volga genomes have illuminated the connections to the Yamnaya people, allowing researchers to make informed conclusions about language divergence and spread. This multidisciplinary approach not only strengthens linguistic hypotheses but also provides a biological foundation for understanding human migrations and cultural exchange.
Genealogical analyses have profoundly altered our perspectives on how we interpret linguistic similarities and differences among Indo-European languages. When researchers correlate these genetic findings with linguistic patterns, it highlights historically significant interactions that would otherwise go unnoticed. The collaborative advancements of geneticists and linguists underscore the dynamic interplay between language and genetic heritage, revealing the multifaceted nature of human development.
Challenges in Understanding Ancient Linguistic Divergence
Despite the groundbreaking discoveries regarding the origins of Indo-European languages, the complexities of ancient linguistic divergence present ongoing challenges. The existence of languages like those in the Anatolian branch raises questions about their emergence and relationship with the Yamnaya lineage. As researchers grapple with finding genetic links to these extinct languages, the task of reconstructing their historical narratives becomes increasingly complex, highlighting the limitations of existing models.
Ancient communities left limited records, making genetic and linguistic correlations critical to understanding their legacy. Innovative analytical methods are required to piece together these fragments of the past, as they not only reveal connections to the Yamnaya but also explore deeper roots in human history. The challenge lies in bridging these gaps and the necessity for collaboration between researchers across multiple disciplines to truly illuminate the puzzle of linguistic development.
Cultural Innovations of the Yamnaya Civilization
The cultural innovations of the Yamnaya civilization played a crucial role in shaping the trajectory of language and social structure across Europe. Their advancements in pastoralism, particularly the domestication of horses and the invention of wagons, not only transformed transportation but also laid the groundwork for new forms of communication and social organization. This evolution in cultural practices is directly linked to the spread of language and ideas among cultures, as the Yamnaya interconnected various communities across vast territories.
Understanding these cultural shifts is essential for grasping how languages evolved over time. The Yamnaya’s adaptation to diverse environments and their interaction with adjacent populations facilitated a hybridization of languages and cultures. As researchers continue to explore these innovations, the profound influence of the Yamnaya on subsequent civilizations and languages becomes evident, showcasing a rich backdrop against which the story of Indo-European languages unfolds.
The Role of the Eurasian Steppes in Language Spread
The Eurasian steppes have historically served as a pivotal conduit for the spread of languages, facilitating interactions among various nomadic and sedentary populations. The movement of the Yamnaya and their cultural descendants across these expansive grasslands exemplifies how geography can shape linguistic evolution. As they traversed the steppe, they carried their languages with them, contributing to the linguistic mash-up that would later give rise to the diverse Indo-European languages we recognize today.
These vast terrains not only provided the economic foundation for pastoralist societies but also allowed for unparalleled cultural exchange, as different groups encountered one another. The steppes acted as a melting pot of ideas, practices, and languages, which profoundly influenced the formation of emerging patterns seen in both ancient and modern tongues. As we study these historical movements, the importance of the Eurasian steppes in the complex tapestry of language evolution becomes undeniable.
Implications of Yamnaya Ancestry on Modern Europeans
Understanding the Yamnaya ancestry and its implications for modern Europeans reveals a significant aspect of our collective identity. Genetic data indicate that a large portion of European populations can trace their lineage back to the Yamnaya, highlighting the pivotal role these ancient peoples played in shaping the demographic landscape of Europe. This genetic legacy continues to influence cultural identities, regional dialects, and even linguistic diversity throughout the continent.
The ramifications extend beyond genetics; they prompt a reevaluation of cultural narratives, illustrating how historical migrations have shaped contemporary societies. This informs ongoing discussions surrounding nationalism and identity in modern Europe, suggesting that our shared ancestry can foster greater intercultural understanding. By integrating findings related to Yamnaya ancestry into contemporary discourse, we can gain a richer appreciation for the interconnectedness of human culture, language, and heritage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the linguistic origins of Indo-European languages?
The linguistic origins of Indo-European languages trace back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people in modern-day Russia, approximately 6,500 years ago. Recent DNA research indicates that these early speakers of the ancestor tongue were pivotal in the evolution of more than 400 Indo-European languages, influencing cultures across Europe and parts of Asia.
How did the Yamnaya culture contribute to Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya culture, which emerged around 5,000 years ago, played a crucial role in the spread of Indo-European languages. As nomadic pastoralists, the Yamnaya expanded their territory from the steppe regions of Eastern Europe to various parts of the continent, bringing their language and cultural practices along, which were linked to the earlier Caucasus Lower Volga people.
What is Proto-Indo-European and its significance?
Proto-Indo-European is the reconstructed ancestor language of the Indo-European family, believed to have been spoken by the Caucasus Lower Volga people. It is significant as it serves as the foundation from which languages like Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit evolved, highlighting the historical connections among these diverse languages.
How does ancient DNA research inform our understanding of Indo-European languages?
Ancient DNA research has revealed critical insights into the demographics and cultural interactions among the Caucasus Lower Volga people and their descendants, the Yamnaya. This research supports the steppe hypothesis, linking genetic evidence with the dispersal of Indo-European languages across Europe and points toward a unified genetic picture of their origins.
What role did the Caucasus region play in the development of Indo-European languages?
The Caucasus region was pivotal in the development of Indo-European languages, serving as a cultural and linguistic crossroads. The Caucasus Lower Volga people, identified through ancient DNA research, are recognized as key originators of these languages, showcasing how migration and genetic mixing contributed to the language family’s evolution.
Why is the Yamnaya’s method of burial significant to linguistic research?
The Yamnaya’s burial practices, specifically their use of kurgans (barrow tombs), provide archaeological evidence that assists researchers in understanding their cultural identity and connections to the Caucasus Lower Volga people. This connection helps trace the geographical and linguistic spread of Indo-European languages over time.
What is the significance of the discoveries related to Indo-European languages in recent studies?
Recent studies highlight the first genetic picture unifying all Indo-European languages, linking the Caucasus Lower Volga people and the Yamnaya as originators. These discoveries are significant as they not only provide clarity on the linguistic origins but also enhance our understanding of the cultural dissemination across vast geographical areas.
How have historical narratives surrounding Indo-European languages evolved?
Historical narratives surrounding Indo-European languages have evolved significantly with the integration of genetic research. Initial theories based on linguistic similarities have been greatly enriched by scientific findings, particularly those identifying the Caucasus Lower Volga people’s role in the linguistic lineage, thereby reshaping our understanding of language evolution and cultural interactions.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The origin of Indo-European languages is traced back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people in present-day Russia, around 6,500 years ago. |
| These languages are spoken by over 40% of the world’s population today. |
| The researchers combined linguistic, archaeological, and genetic evidence to identify this group’s significance. |
| The Yamnaya people were previously considered the main contributors to the spread of Indo-European languages. |
| Findings were published in the journal Nature, including DNA analysis from 435 ancient individuals. |
| The research illustrates migrations of these ancient groups and their interactions with other populations. |
| Challenges in research collaboration were noted, particularly due to the Russia-Ukraine conflict. |
| The study emphasizes the significance of cultural traditions, e.g., burial practices linking ancient peoples. |
Summary
Indo-European languages have a profound historical and cultural significance, impacting over 40% of the global population. Recent studies utilizing genetic analysis have pinpointed the origins of these languages to a group known as the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who lived around 6,500 years ago in today’s Russia. This research has opened new avenues for understanding how ancient civilizations influenced language, culture, and migration patterns across vast territories from Europe to Asia. As scholars continue to uncover the connections between genetics and linguistics, the story of Indo-European languages grows ever richer.